The DevSecOps Journey Begins with Identity
Summary
This article delves into the foundational role of identity in the DevSecOps journey, asserting that a strong grasp of software security is essential for effective security practices beyond mere tooling. I highlight that security is an exercise in paranoia, demanding a deep interrogation of true risks rather than relying solely on automated scanners. As a DevOps practitioner and technical writer, I aim to demystify security concepts, focusing on identity as the first fundamental principle.
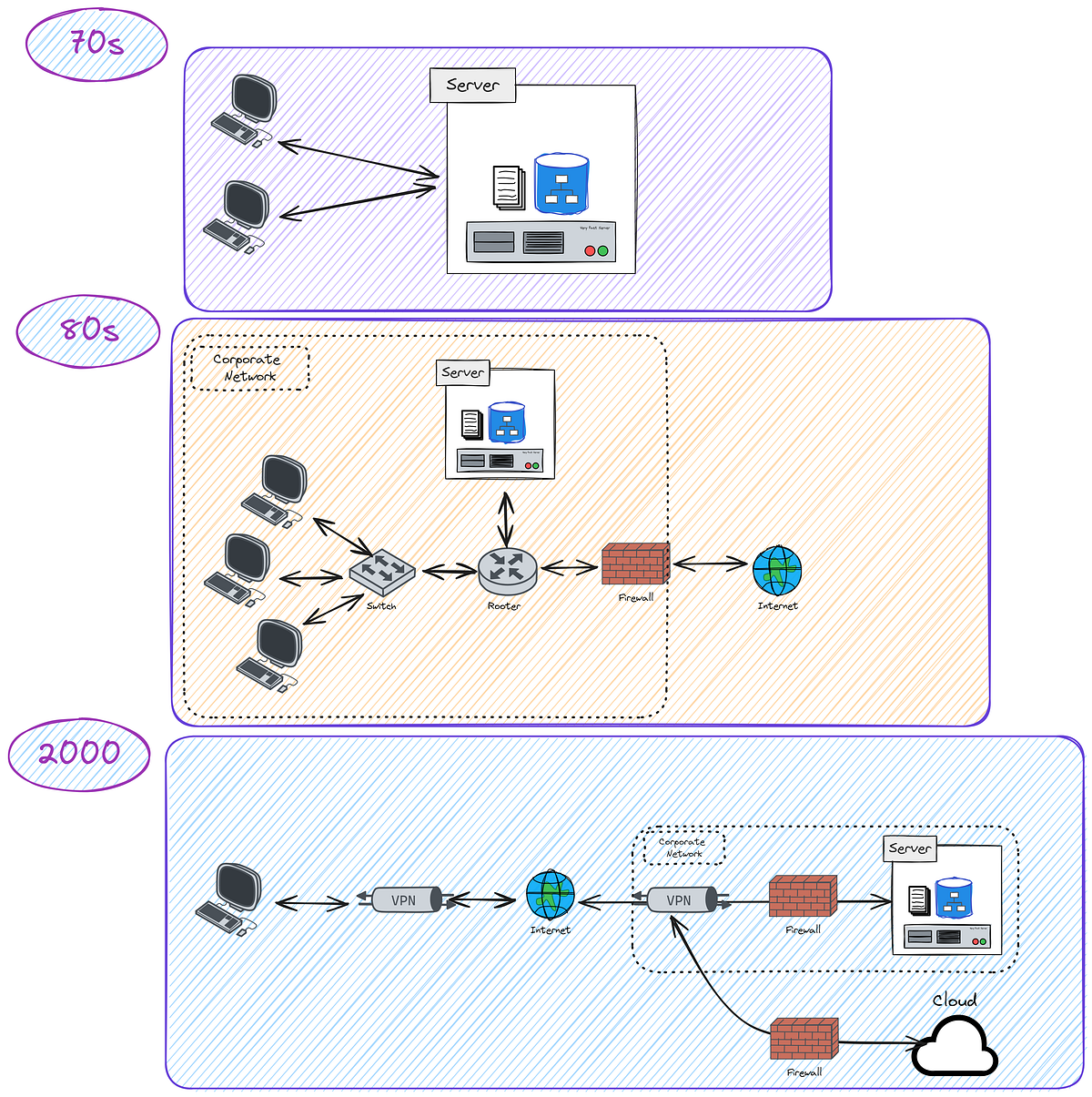
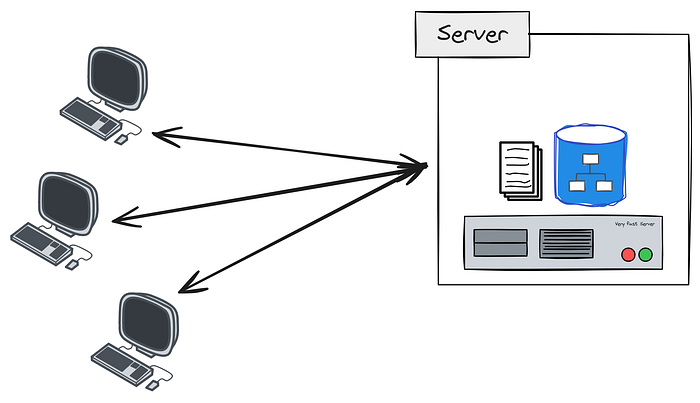
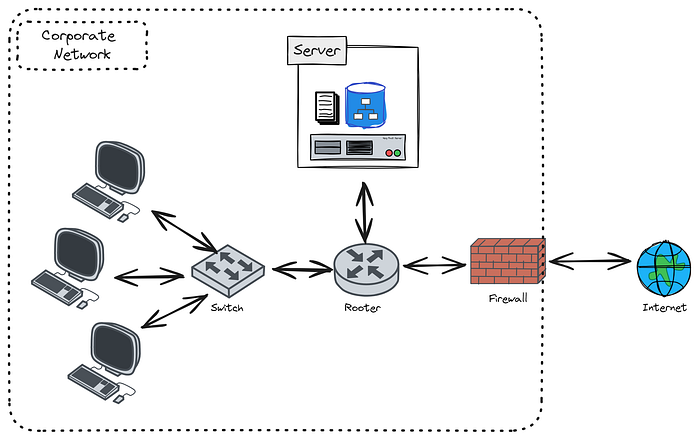
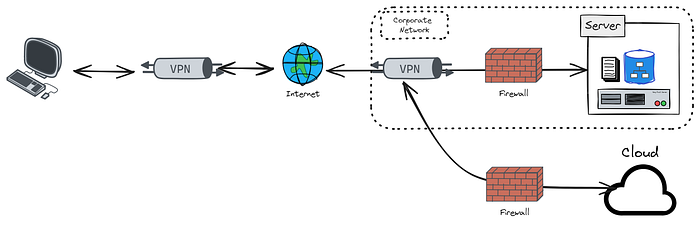
You will explore the historical evolution of identity in software systems, from early Client-Server models with basic user accounts to the Network Perimeter era with centralized systems like Active Directory, and finally to modern Distributed and Cloud-Based Systems utilizing technologies like SAML, OpenID Connect, and SSO.
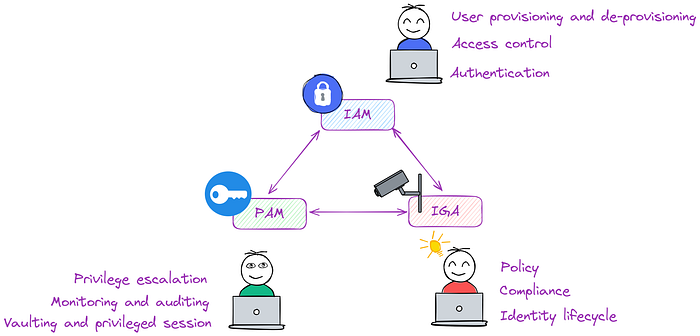
The article then examines the three critical domains of identity management: Identity and Access Management (IAM), which focuses on regulating user identities and access privileges; Privileged Access Management (PAM), crucial for securing accounts with elevated permissions to sensitive data; and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA), which establishes the comprehensive framework for managing identities throughout their lifecycle. I argue that while IAM is well-known, companies often struggle with effectively implementing PAM and IGA.
Finally, I introduce the Zero Trust security approach, a paradigm shift from traditional perimeter-based security. This approach operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” requiring continuous verification for every access attempt, regardless of its origin. By embracing robust identity management practices and the Zero Trust model, you can significantly enhance your DevSecOps efforts and ensure the integrity of your software development process.
Key Concepts
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Manages user identities, access privileges, and authentication methods (e.g., MFA). It ensures only authorized users access resources.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Secures accounts with elevated permissions to critical systems and sensitive data. Key features include privilege escalation workflows, secure credential vaulting, and session monitoring, always adhering to the least privilege principle.
- Identity Governance and Administration (IGA): Provides the overarching framework for managing identities from creation to deletion. It ensures policy definition and enforcement, compliance management, and streamlined identity lifecycle management.
- Zero Trust: A security model that assumes no implicit trust, even within the network. It requires continuous verification for every access attempt, regardless of the source.