Securely Managing Secrets in Pipelines CI/CD
Original Article: Securely Managing Secrets in Pipelines CI/CD
Summary
In this article, I explore the critical aspects of securely managing secrets within your CI/CD pipelines. I guide you through three main approaches: encrypted secrets, secret vaults, and short-lived credentials, detailing their advantages and disadvantages. This understanding will help you safeguard sensitive data like passwords and API tokens, ensuring a more secure software development lifecycle. I also emphasize three golden rules for secret management: adhering to the Least Access Principle, maintaining a Short Secret Lifecycle, and always remembering to Never share secrets.
Key Concepts
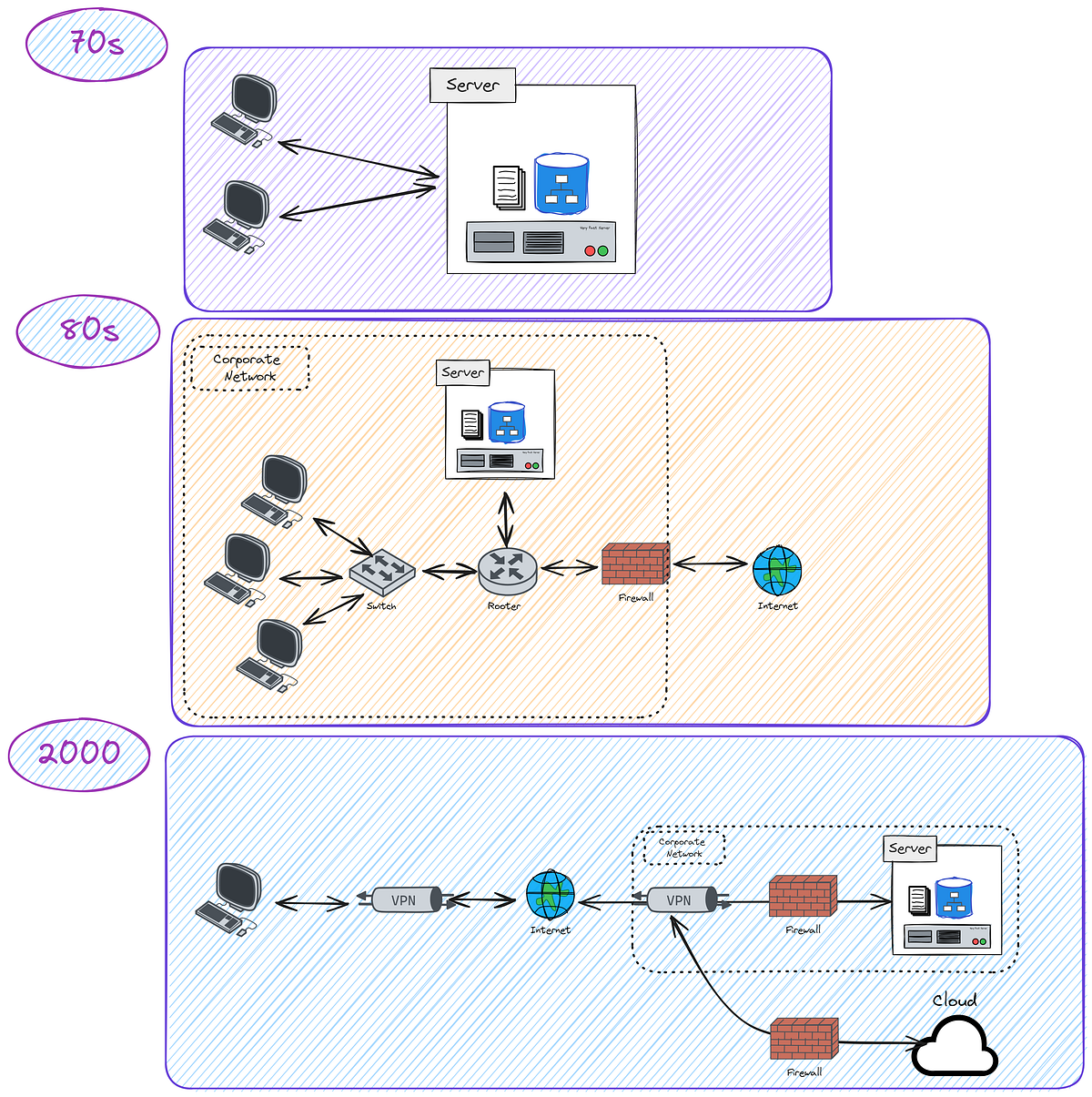
- Encrypted/Sealed Secrets: An older, simpler method where secrets are encrypted in repositories. The main vulnerability lies in key management.
- Secret Vaults: The current industry standard for centralized secret storage, offering robust security features and access controls (e.g., CI Provider Vaults, Cloud Provider Vaults, HashiCorp Vault). While effective, they don’t inherently enforce least privilege or frequent secret rotation.
- Short-lived Credentials: The most advanced and recommended approach, involving temporary access tokens that expire after use. This method, often facilitated by protocols like OpenID Connect (OIDC), eliminates the need for persistent secrets by relying on pipeline identity validation.